Configuring your IoT device
GNSS and APNT configuration.
Currently, the primary configuration function of the app is focused on GNSS and APNT positioning functionality.
All settings can also be made within the User Configuration file or remotely via Cloudloop device manager.
APNT is not fitted as standard. Only available on the APNT version of the RockBLOCK Pro
Full device configuration details available here:
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
NOTE that for settings to take effect the APPLY button in the top right needs to be pressed.
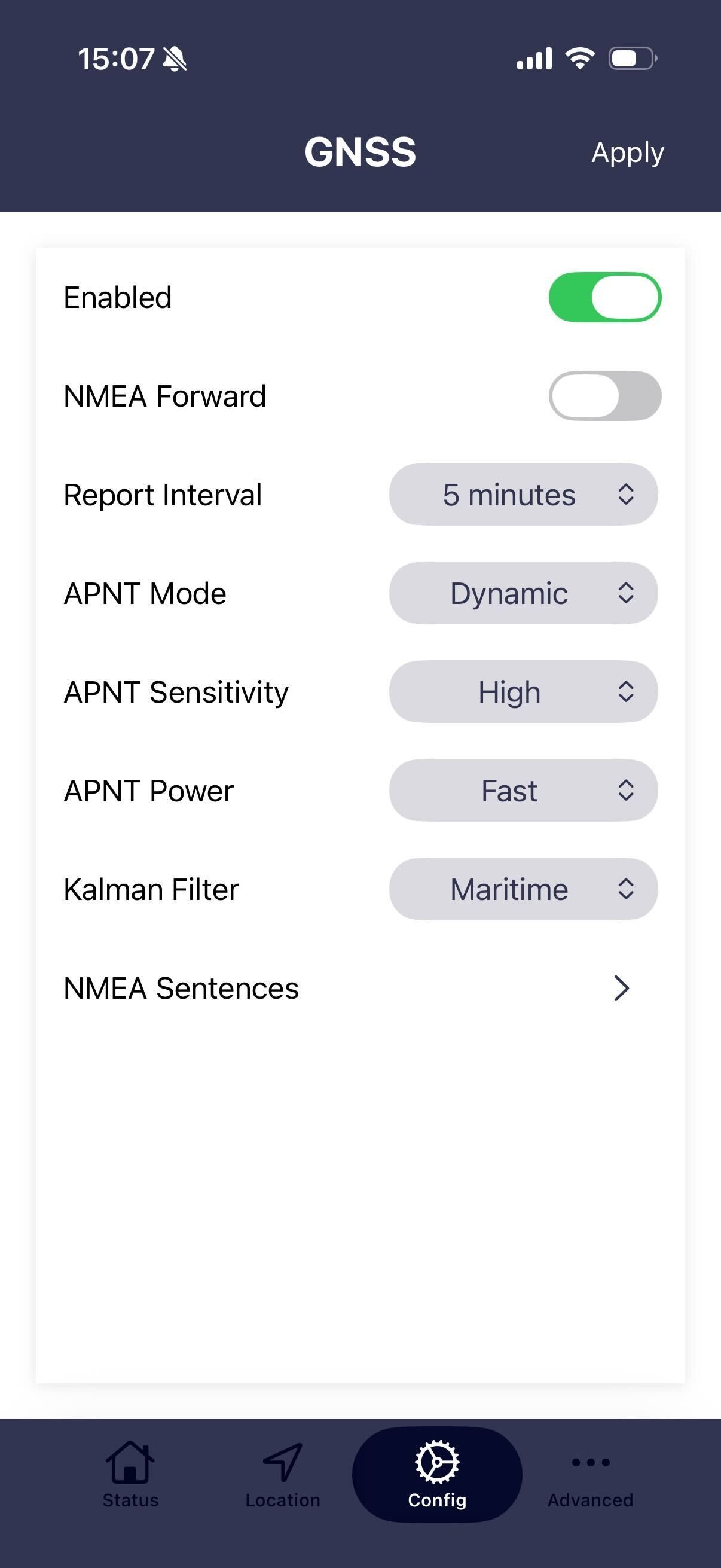
Enabled
When enabled the RB-Pro APNT will begin reporting both APNT and GNSS positions to Cloudloop with the set interval.
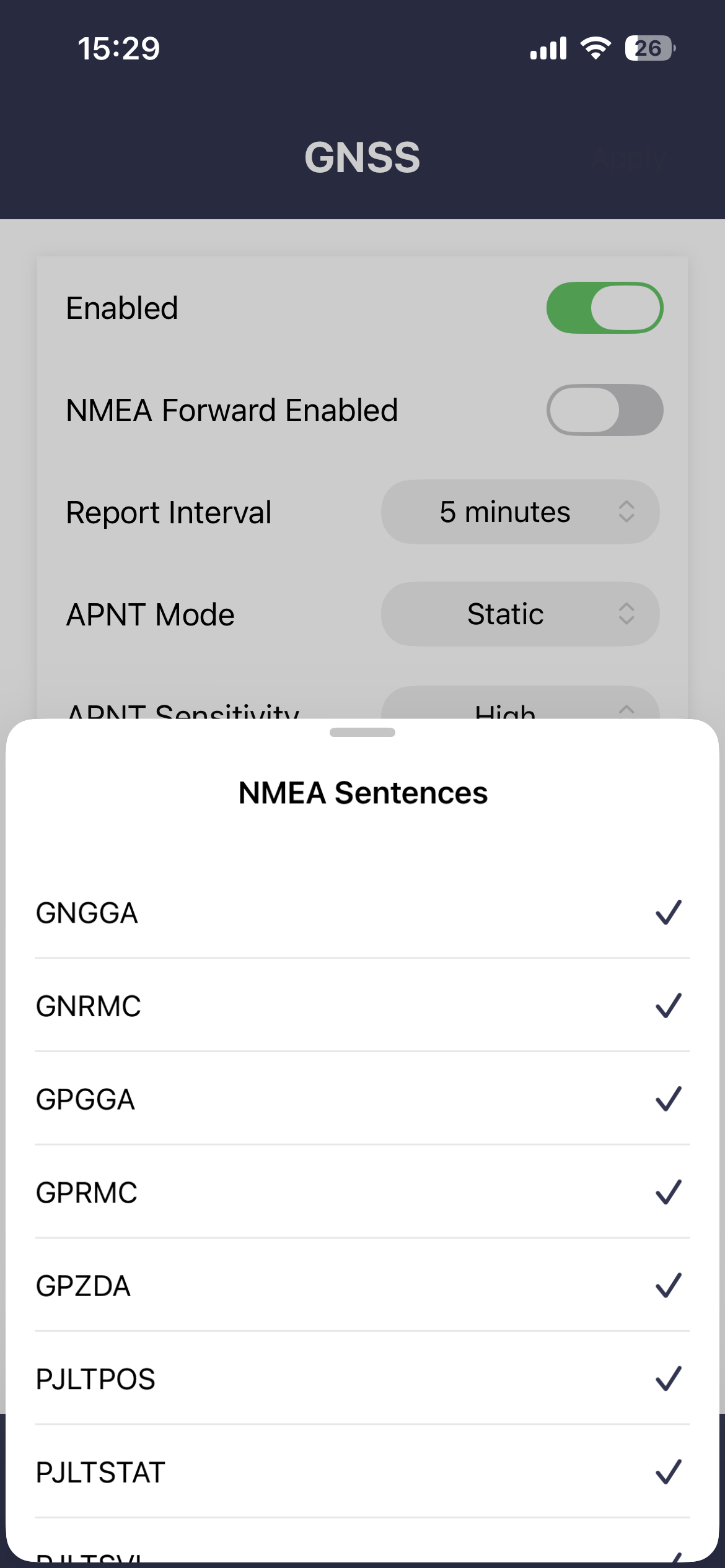
NMEA forward enabled
When enabled the selected sentences will be streamed on the serial interface. Most sentences are streamed every second or when available. PJLTSVI is only streamed on receipt of an APNT burst.
Report interval
Set's the interval between each APNT and GNSS position reports to Cloudloop. The setting will correct to the nearest whole denomination of time. i.e. for 1 hour it will be at the top of the hour etc.
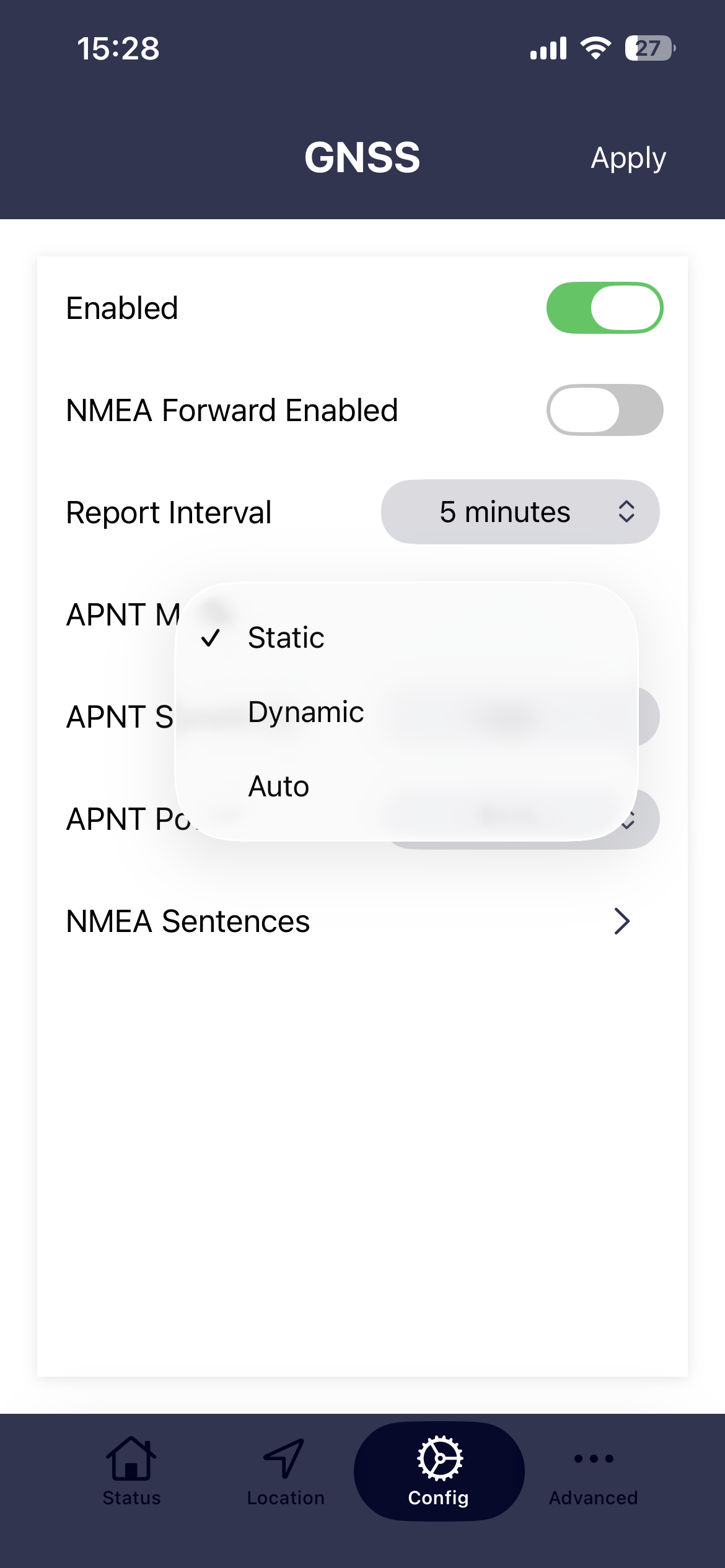
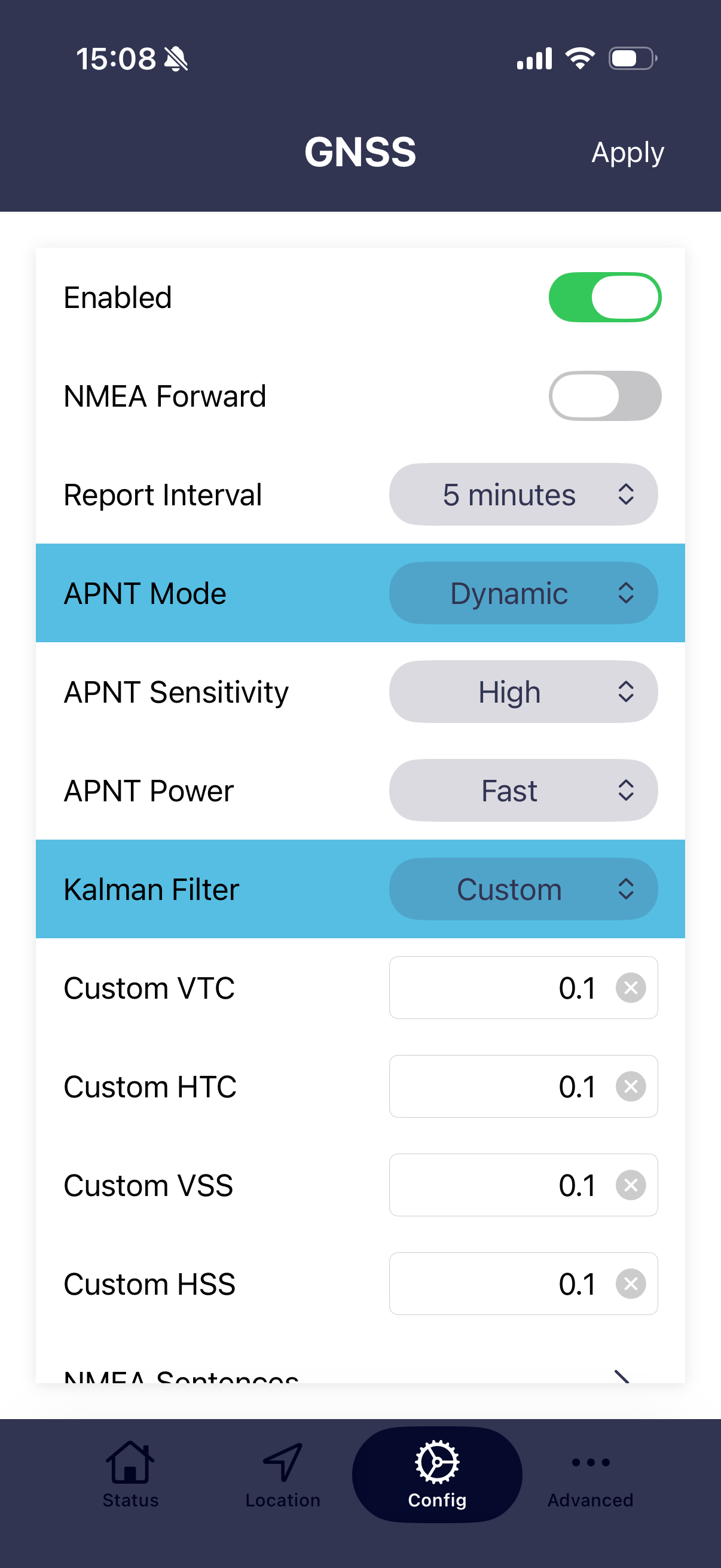
APNT modes
- Static. The device assumes that it remains in a fixed position. Kalman filter pre-sets or custom settings are not applied. Over time, Static mode will arrive at the most accurate time and position.
- Dynamic. Applies the Kalman filter pre-set or custom settings to better track a moving object.
- Auto. Auto mode uses GNSS source to determine if receiver is moving to automatically switch between static and dynamic mode.
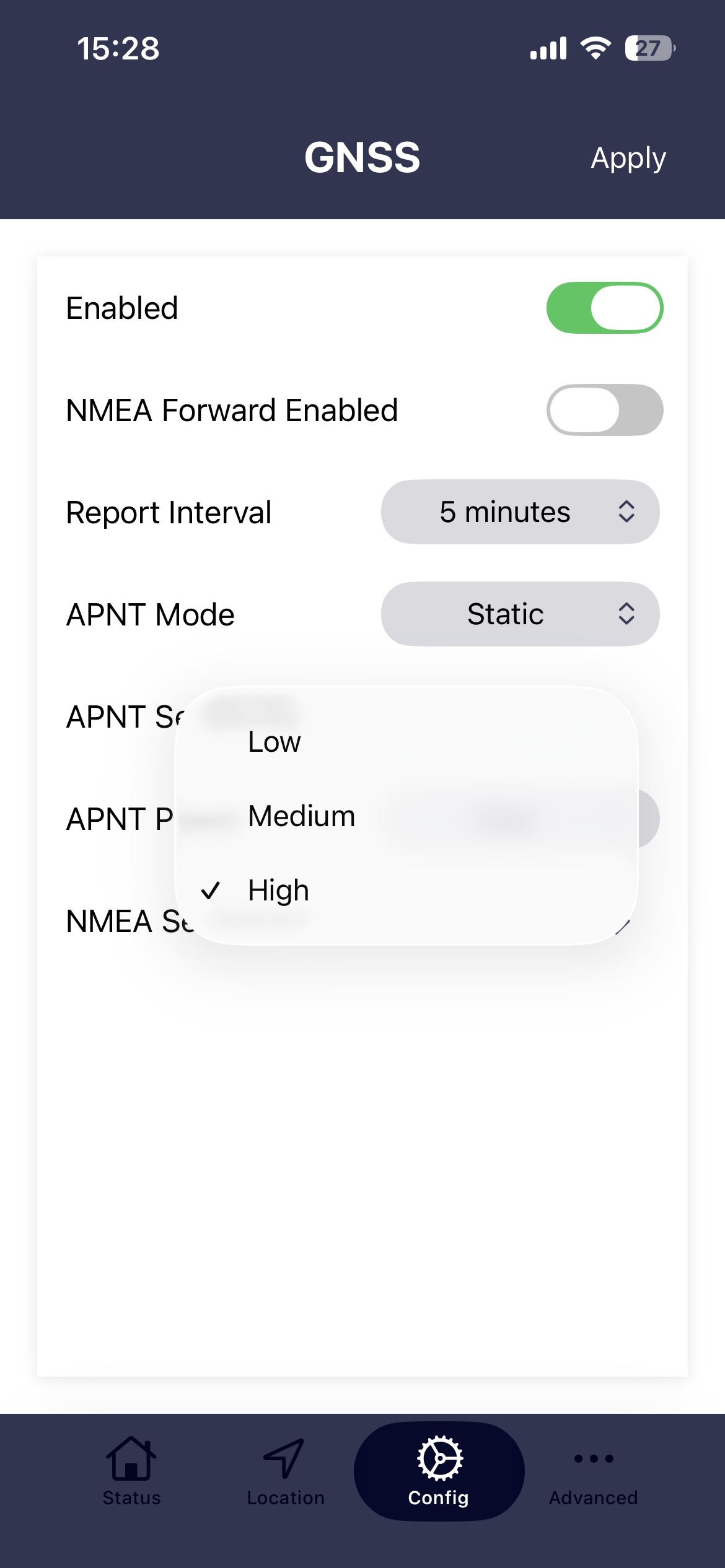
APNT sensitivity
This setting controls the gain of the receiver pre-amplifier. High sensitivity will give the best results when indoors or in areas with a restricted view of the sky. However, when a very high rate of Iridium STL® bursts are available there can be advantages in lowering the sensitivity as this helps to reject bursts that have a degraded measurement quality. This will improve timing and positioning accuracy.
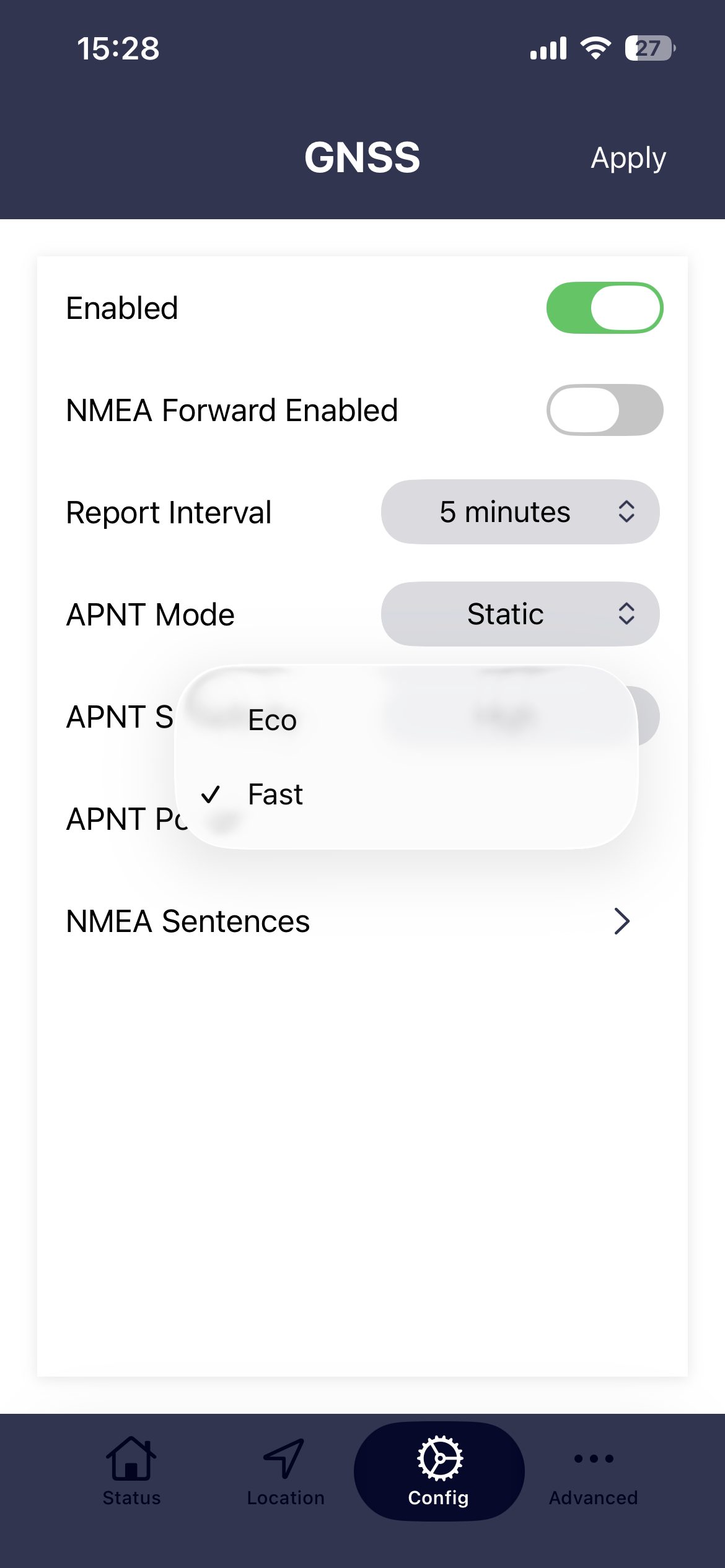
APNT power(saving)
- Fast This setting will give the best performance as ALL of the APNT modules power saving features will be turned off.
- Eco Enables all of the APNT modules power saving features. Power saving will be between 300mW to 500mW. Note that one of the power saving features is to turn OFF the GNSS receiver so for any application that uses GNSS (i.e. if the APNT mode is set to Auto, the APNT power(saving) must be set to off)
APNT Kalman profiles
- Custom. Allows the user to set Kalman filter settings to better suit a particular application.
- Maritime. These settings are recommended for larger vessels.
- Walking. Tracking personnel on foot.
- Driving. Vehicle based applications in relatively flat terrain.